linux hard drive test zero out|Linux zero out drive : importers For read/write (-w) and non-destructive (-n) modes, one or more test patterns may be specified by specifying the -t option for each test pattern desired. For read-only mode only a . Autoclave kills microorganisms using saturated stem under pressure. Autoclave comprises of three parts: a pressure chamber, a lid and an electrical heater.
{plog:ftitle_list}
What is an Autoclave? An autoclave is a piece of equipment used in nearly all scientific fields and industries. It uses high-pressure steam to sterilize objects that can withstand the high temperatures. It turns hazardous waste into non-hazardous waste, and it’s responsible for the level of sterilization that’s able to be achieved today.Autoclave tape works by changing color after exposure to temperatures commonly used in sterilization processes, typically 121°C in a steam autoclave. Small strips of the tape are applied to the items before they are placed into the autoclave.

Zero-out drive on Linux is done via: dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdX where sdX is the device of the drive to delete. If you're not aware on how to do this, press Ctrl+Alt+T from Ubuntu, and type following: sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdb In example above, sdb is the second connected . For read/write (-w) and non-destructive (-n) modes, one or more test patterns may be specified by specifying the -t option for each test pattern desired. For read-only mode only a . I have a large drive (4TB) that I've only written a few gigabytes to. I'm giving it to a friend, so I'd like to zero it out. I know I can zero out the whole drive with dd, but I'd like to .Assuming a fairly recent computer with middle-grade drives, on a minimal linux boot disk running JUST the zeroing operation (no gui, internet, etc) loaded entirely to RAM, it could be anywhere .
1. dtstat. All five commands provide useful ways to view disk activity. Probably one of the easiest and most obvious of these commands is dstat. In spite of the fact that the dstat .
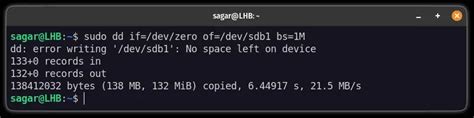
Alternatively, if I wanted to zero out the drives, I could do so with: # dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdX bs=1M. While doing so, I could monitor the SMART attributes for any drastic .If the drive doesn't have a file system (and only then), use of=/dev/sda. Otherwise, mount it on /tmp and write then delete the test output file. dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/output bs=8k count=10k; rm -f /tmp/output 10240+0 .
With that in mind, you’ll need to use a Linux live DVD or USB to allow you to zero fill a hard drive. These are portable Linux environments that allow you to test distributions out before installing them, but we’ll be using . sudo mount /dev/loopXXX /mnt/test. Copy your program on that partition and test. cp /path/my/program /mnt/test && cd /mnt/test && ./program. Substitute /dev/loopXXX with the .Zero-out drive on Linux is done via: dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdX where sdX is the device of the drive to delete. If you're not aware on how to do this, press Ctrl+Alt+T from Ubuntu, and type following: sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdb In example above, sdb is the second connected drive. NB! This will erase your drive completely. Use at your own . hdparm command : It is used to get/set hard disk parameters including test the reading and caching performance of a disk device on a Linux based system. In this tutorial you will learn how to use the dd command to test disk I/O performance .
ubuntu zero out drive
For read/write (-w) and non-destructive (-n) modes, one or more test patterns may be specified by specifying the -t option for each test pattern desired. For read-only mode only a single pattern may be specified and it may not be "random". I have a large drive (4TB) that I've only written a few gigabytes to. I'm giving it to a friend, so I'd like to zero it out. I know I can zero out the whole drive with dd, but I'd like to know if: zeroing only the non-zero bits will be faster, and. if so, how to go about doing that.Assuming a fairly recent computer with middle-grade drives, on a minimal linux boot disk running JUST the zeroing operation (no gui, internet, etc) loaded entirely to RAM, it could be anywhere from 2-12 hours.
1. dtstat. All five commands provide useful ways to view disk activity. Probably one of the easiest and most obvious of these commands is dstat. In spite of the fact that the dstat command begins . dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdX bs=1M. dd copies bits from "if" to "of". Blocksize 1M is usually a good value for performance. Repace sdX with your actual drive. If you need to track progress, install "pv" (pipeviewer) pv /dev/zero > /dev/sdX. Alternatively, if I wanted to zero out the drives, I could do so with: # dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdX bs=1M. While doing so, I could monitor the SMART attributes for any drastic changes. The drives have already been up for 24 hours per @sawdust's recommendation, and I observed the SMART attributes during this time.If the drive doesn't have a file system (and only then), use of=/dev/sda. Otherwise, mount it on /tmp and write then delete the test output file. dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/output bs=8k count=10k; rm -f /tmp/output 10240+0 records in 10240+0 records out 83886080 bytes (84 MB) copied, 1.08009 s, 77.7 MB/s Graphical method
With that in mind, you’ll need to use a Linux live DVD or USB to allow you to zero fill a hard drive. These are portable Linux environments that allow you to test distributions out before installing them, but we’ll be using them for a slightly different purpose.
Zero-out drive on Linux is done via: dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdX where sdX is the device of the drive to delete. If you're not aware on how to do this, press Ctrl+Alt+T from Ubuntu, and type following: sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdb In example above, sdb is the second connected drive. NB! This will erase your drive completely. Use at your own .
hdparm command : It is used to get/set hard disk parameters including test the reading and caching performance of a disk device on a Linux based system. In this tutorial you will learn how to use the dd command to test disk I/O performance . For read/write (-w) and non-destructive (-n) modes, one or more test patterns may be specified by specifying the -t option for each test pattern desired. For read-only mode only a single pattern may be specified and it may not be "random".
describe autoclaving process
I have a large drive (4TB) that I've only written a few gigabytes to. I'm giving it to a friend, so I'd like to zero it out. I know I can zero out the whole drive with dd, but I'd like to know if: zeroing only the non-zero bits will be faster, and. if so, how to go about doing that.Assuming a fairly recent computer with middle-grade drives, on a minimal linux boot disk running JUST the zeroing operation (no gui, internet, etc) loaded entirely to RAM, it could be anywhere from 2-12 hours. 1. dtstat. All five commands provide useful ways to view disk activity. Probably one of the easiest and most obvious of these commands is dstat. In spite of the fact that the dstat command begins .
describe the use of an autoclave in microbiology laboratory
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdX bs=1M. dd copies bits from "if" to "of". Blocksize 1M is usually a good value for performance. Repace sdX with your actual drive. If you need to track progress, install "pv" (pipeviewer) pv /dev/zero > /dev/sdX. Alternatively, if I wanted to zero out the drives, I could do so with: # dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdX bs=1M. While doing so, I could monitor the SMART attributes for any drastic changes. The drives have already been up for 24 hours per @sawdust's recommendation, and I observed the SMART attributes during this time.If the drive doesn't have a file system (and only then), use of=/dev/sda. Otherwise, mount it on /tmp and write then delete the test output file. dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/output bs=8k count=10k; rm -f /tmp/output 10240+0 records in 10240+0 records out 83886080 bytes (84 MB) copied, 1.08009 s, 77.7 MB/s Graphical method
how to zero out a drive
Linux zero out drive
An autoclave is a machine that provides a physical method of sterilization by killing bacteria, viruses, and even spores present in the material put inside of the vessel using steam under pressure. Autoclave sterilizes the materials by heating them up to a particular temperature for a specific period of time.
linux hard drive test zero out|Linux zero out drive